Need for Building Information Modelling

Building Information Modeling (BIM) is of significant importance in the construction industry for various reasons. Here are a few key explanations why BIM is essential:
Improved Collaboration: BIM promotes collaboration and coordination among various stakeholders involved in the construction project, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. By utilizing a shared digital model, stakeholders could work together more efficiently, reducing errors, conflicts, and rework.
Enhanced Visualization and Communication: BIM provides a visual representation of the building or infrastructure project, allowing stakeholders to better understand the look intent. This helps to make informed decisions, resolving conflicts, and effectively communicating the project details to all parties involved, including clients and contractors.
Building Information Modelling Kidderminster and Conflict Resolution: BIM enables clash detection by overlaying different building systems and components within the model. This can help identify conflicts and clashes, such as clashes between structural elements, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems, or spatial conflicts. Early detection of clashes through BIM reduces rework and costly on-site modifications during construction.
Improved Design Accuracy: BIM permits more accurate and precise design documentation. It enables designers to create detailed and coordinated 3D models, that may be further enriched with additional information such as for example specifications, quantities, and cost data. This helps in achieving better design accuracy, reducing errors, and optimizing the construction process.
Cost and Time Savings: BIM facilitates better project planning, estimation, and scheduling. By integrating cost and scheduling information within the BIM model, stakeholders can identify potential cost overruns, optimize construction sequencing, and make informed decisions to save time and resources. BIM also supports off-site fabrication and prefabrication, reducing on-site construction time and improving productivity.
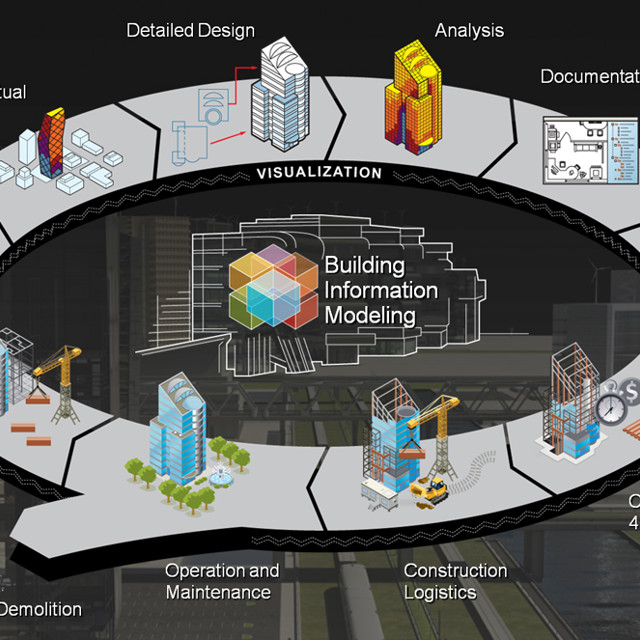
Facilities Management and Maintenance: BIM extends its benefits beyond the construction phase in to the operation and maintenance of buildings. The digital model created during the design and construction process can be utilized for facilities management, including asset tracking, maintenance planning, and energy analysis. BIM data can help optimize building performance, reduce operational costs, and support sustainability initiatives.
Future Expansion and Renovation: BIM provides a valuable resource for future expansion, renovation, or retrofitting of buildings. The accurate as-built information captured in the BIM model serves as a foundation for future modifications, reducing the effort and cost associated with gathering information about existing conditions.
Overall, BIM improves collaboration, reduces errors, enhances project visualization, and facilitates more efficient and cost-effective construction processes. It has become an essential tool in the construction industry, driving innovation and improving project outcomes through the entire entire lifecycle of a building.
